Archive for the ‘MS Office & VBA’ Category.
2017-12-13, 21:51
Datumswerte der Form (d)dmmjjjj, also beispielsweise 1122017 für den 1.12.2017 lassen sich leicht durch die folgende Excel-Funktion in etwas brauchbares verwandeln:
=WERT(WECHSELN(B4;LINKS(RECHTS(B4;6);2)&RECHTS(B4;4);"")&"."&LINKS(RECHTS(B4;6);2)&"."&RECHTS(B4;4)) |
=WERT(WECHSELN(B4;LINKS(RECHTS(B4;6);2)&RECHTS(B4;4);"")&"."&LINKS(RECHTS(B4;6);2)&"."&RECHTS(B4;4))
Annahme: Der „schlechte“ Datumsstring steht in Zelle B4. Das erzeugte Ergebnis muss man dann über die Formatierung auf Datum ändern.
Hier zur Erläuterung:
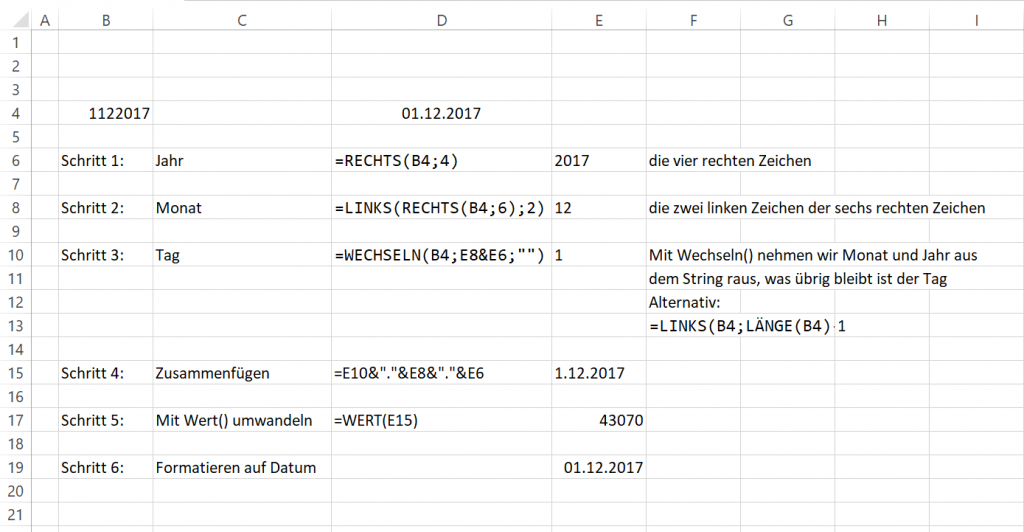
Beispiel-Excel:
DatumUmwandeln
Die finale Formel, die oben angegeben ist, fügt die einzelnen Teile nur zusammen.
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2017-12-10, 19:32
Ich muss mich gelegentlich mit MS Access beschäftigen und habe eine Möglichkeit gesucht, Tabellenstrukturen zu exportieren. Basierend auf Code von Allen Browne (http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html) habe ich um seine TableInfo() Funktion eine Exportfunktion geschrieben.
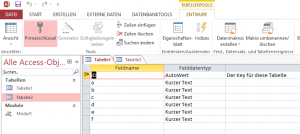
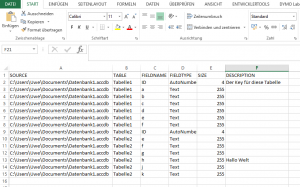
Option Compare Database
' based on http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
' modified for the export of the information by Uwe Ziegenhagen
Sub exportTableInformation()
On Error GoTo TableInfoErr
' Purpose: Display the field names, types, sizes and descriptions for a table.
' Argument: Name of a table in the current database.
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim tdf As DAO.TableDef
Dim fld As DAO.Field
Set db = CurrentDb()
' ask user for path of the output file
' https://support.office.com/de-de/article/InputBox-Funktion-Eingabefeld-17821927-28b7-4350-b7f1-4786575314d9
Dim Message, Title, Default, MyValue
Message = "File will be overwritten..." ' Set prompt.
Title = "Enter file of output file" ' Set title.
Default = "c:\somefile.csv" ' Set default.
' Display message, title, and default value.
outputfilePath = InputBox(Message, Title, Default)
n = FreeFile()
Open outputfilePath For Output As #n
Print #n, "SOURCE;TABLE;FIELDNAME;FIELDTYPE;SIZE;DESCRIPTION"
Set db = CurrentDb()
Debug.Print
For Each tdf In db.TableDefs
' ignore system and temporary tables
If Not (tdf.Name Like "MSys*" Or tdf.Name Like "~*") Then
For Each fld In tdf.Fields
Debug.Print db.Name & ";" & tdf.Name & ";" & fld.Name & ";" & FieldTypeName(fld) & ";" & fld.Size & ";" & GetDescrip(fld)
Print #n, db.Name & ";" & tdf.Name & ";" & fld.Name & ";" & FieldTypeName(fld) & ";" & fld.Size & ";" & GetDescrip(fld)
Next
End If
Next
Set tdf = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
Close #n
TableInfoExit:
Set db = Nothing
Exit Sub
TableInfoErr:
Select Case Err
Case 3265& 'Table name invalid
MsgBox strTableName & " table doesn't exist"
Case Else
Debug.Print "TableInfo() Error " & Err & ": " & Error
End Select
Resume TableInfoExit
End Sub
Function GetDescrip(obj As Object) As String
' http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
On Error Resume Next
GetDescrip = obj.Properties("Description")
End Function
Function FieldTypeName(fld As DAO.Field) As String
'http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
'Purpose: Converts the numeric results of DAO Field.Type to text.
Dim strReturn As String 'Name to return
Select Case CLng(fld.Type) 'fld.Type is Integer, but constants are Long.
Case dbBoolean: strReturn = "Yes/No" ' 1
Case dbByte: strReturn = "Byte" ' 2
Case dbInteger: strReturn = "Integer" ' 3
Case dbLong ' 4
If (fld.Attributes And dbAutoIncrField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Long Integer"
Else
strReturn = "AutoNumber"
End If
Case dbCurrency: strReturn = "Currency" ' 5
Case dbSingle: strReturn = "Single" ' 6
Case dbDouble: strReturn = "Double" ' 7
Case dbDate: strReturn = "Date/Time" ' 8
Case dbBinary: strReturn = "Binary" ' 9 (no interface)
Case dbText '10
If (fld.Attributes And dbFixedField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Text"
Else
strReturn = "Text (fixed width)" '(no interface)
End If
Case dbLongBinary: strReturn = "OLE Object" '11
Case dbMemo '12
If (fld.Attributes And dbHyperlinkField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Memo"
Else
strReturn = "Hyperlink"
End If
Case dbGUID: strReturn = "GUID" '15
'Attached tables only: cannot create these in JET.
Case dbBigInt: strReturn = "Big Integer" '16
Case dbVarBinary: strReturn = "VarBinary" '17
Case dbChar: strReturn = "Char" '18
Case dbNumeric: strReturn = "Numeric" '19
Case dbDecimal: strReturn = "Decimal" '20
Case dbFloat: strReturn = "Float" '21
Case dbTime: strReturn = "Time" '22
Case dbTimeStamp: strReturn = "Time Stamp" '23
'Constants for complex types don't work prior to Access 2007 and later.
Case 101&: strReturn = "Attachment" 'dbAttachment
Case 102&: strReturn = "Complex Byte" 'dbComplexByte
Case 103&: strReturn = "Complex Integer" 'dbComplexInteger
Case 104&: strReturn = "Complex Long" 'dbComplexLong
Case 105&: strReturn = "Complex Single" 'dbComplexSingle
Case 106&: strReturn = "Complex Double" 'dbComplexDouble
Case 107&: strReturn = "Complex GUID" 'dbComplexGUID
Case 108&: strReturn = "Complex Decimal" 'dbComplexDecimal
Case 109&: strReturn = "Complex Text" 'dbComplexText
Case Else: strReturn = "Field type " & fld.Type & " unknown"
End Select
FieldTypeName = strReturn
End Function |
Option Compare Database
' based on http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
' modified for the export of the information by Uwe Ziegenhagen
Sub exportTableInformation()
On Error GoTo TableInfoErr
' Purpose: Display the field names, types, sizes and descriptions for a table.
' Argument: Name of a table in the current database.
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim tdf As DAO.TableDef
Dim fld As DAO.Field
Set db = CurrentDb()
' ask user for path of the output file
' https://support.office.com/de-de/article/InputBox-Funktion-Eingabefeld-17821927-28b7-4350-b7f1-4786575314d9
Dim Message, Title, Default, MyValue
Message = "File will be overwritten..." ' Set prompt.
Title = "Enter file of output file" ' Set title.
Default = "c:\somefile.csv" ' Set default.
' Display message, title, and default value.
outputfilePath = InputBox(Message, Title, Default)
n = FreeFile()
Open outputfilePath For Output As #n
Print #n, "SOURCE;TABLE;FIELDNAME;FIELDTYPE;SIZE;DESCRIPTION"
Set db = CurrentDb()
Debug.Print
For Each tdf In db.TableDefs
' ignore system and temporary tables
If Not (tdf.Name Like "MSys*" Or tdf.Name Like "~*") Then
For Each fld In tdf.Fields
Debug.Print db.Name & ";" & tdf.Name & ";" & fld.Name & ";" & FieldTypeName(fld) & ";" & fld.Size & ";" & GetDescrip(fld)
Print #n, db.Name & ";" & tdf.Name & ";" & fld.Name & ";" & FieldTypeName(fld) & ";" & fld.Size & ";" & GetDescrip(fld)
Next
End If
Next
Set tdf = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
Close #n
TableInfoExit:
Set db = Nothing
Exit Sub
TableInfoErr:
Select Case Err
Case 3265& 'Table name invalid
MsgBox strTableName & " table doesn't exist"
Case Else
Debug.Print "TableInfo() Error " & Err & ": " & Error
End Select
Resume TableInfoExit
End Sub
Function GetDescrip(obj As Object) As String
' http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
On Error Resume Next
GetDescrip = obj.Properties("Description")
End Function
Function FieldTypeName(fld As DAO.Field) As String
'http://allenbrowne.com/func-06.html
'Purpose: Converts the numeric results of DAO Field.Type to text.
Dim strReturn As String 'Name to return
Select Case CLng(fld.Type) 'fld.Type is Integer, but constants are Long.
Case dbBoolean: strReturn = "Yes/No" ' 1
Case dbByte: strReturn = "Byte" ' 2
Case dbInteger: strReturn = "Integer" ' 3
Case dbLong ' 4
If (fld.Attributes And dbAutoIncrField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Long Integer"
Else
strReturn = "AutoNumber"
End If
Case dbCurrency: strReturn = "Currency" ' 5
Case dbSingle: strReturn = "Single" ' 6
Case dbDouble: strReturn = "Double" ' 7
Case dbDate: strReturn = "Date/Time" ' 8
Case dbBinary: strReturn = "Binary" ' 9 (no interface)
Case dbText '10
If (fld.Attributes And dbFixedField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Text"
Else
strReturn = "Text (fixed width)" '(no interface)
End If
Case dbLongBinary: strReturn = "OLE Object" '11
Case dbMemo '12
If (fld.Attributes And dbHyperlinkField) = 0& Then
strReturn = "Memo"
Else
strReturn = "Hyperlink"
End If
Case dbGUID: strReturn = "GUID" '15
'Attached tables only: cannot create these in JET.
Case dbBigInt: strReturn = "Big Integer" '16
Case dbVarBinary: strReturn = "VarBinary" '17
Case dbChar: strReturn = "Char" '18
Case dbNumeric: strReturn = "Numeric" '19
Case dbDecimal: strReturn = "Decimal" '20
Case dbFloat: strReturn = "Float" '21
Case dbTime: strReturn = "Time" '22
Case dbTimeStamp: strReturn = "Time Stamp" '23
'Constants for complex types don't work prior to Access 2007 and later.
Case 101&: strReturn = "Attachment" 'dbAttachment
Case 102&: strReturn = "Complex Byte" 'dbComplexByte
Case 103&: strReturn = "Complex Integer" 'dbComplexInteger
Case 104&: strReturn = "Complex Long" 'dbComplexLong
Case 105&: strReturn = "Complex Single" 'dbComplexSingle
Case 106&: strReturn = "Complex Double" 'dbComplexDouble
Case 107&: strReturn = "Complex GUID" 'dbComplexGUID
Case 108&: strReturn = "Complex Decimal" 'dbComplexDecimal
Case 109&: strReturn = "Complex Text" 'dbComplexText
Case Else: strReturn = "Field type " & fld.Type & " unknown"
End Select
FieldTypeName = strReturn
End Function
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2017-11-12, 14:55
Hier basierend auf einem Beispiel von Microsoft eine IN-Funktion. Mit dieser lässt sich prüfen, ob ein String in einem zusammengesetzten String enthalten ist.
Option Explicit
Function Contains(needle As String, haystack As String, separator As String) As Boolean
Dim rv As Boolean, lb As Long, ub As Long, i As Long, field() As String
field = Split(haystack, separator)
lb = LBound(field)
ub = UBound(field)
For i = lb To ub
If field(i) = needle Then
rv = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
Contains = rv
End Function |
Option Explicit
Function Contains(needle As String, haystack As String, separator As String) As Boolean
Dim rv As Boolean, lb As Long, ub As Long, i As Long, field() As String
field = Split(haystack, separator)
lb = LBound(field)
ub = UBound(field)
For i = lb To ub
If field(i) = needle Then
rv = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
Contains = rv
End Function
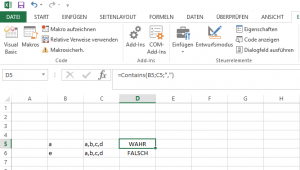
Nachtrag: Möchte man prüfen, ob ein Wert in einer Range vorhanden ist, kann man die folgende User-Defined Function nutzen:
Function InRange(needle As Variant, haystack As Range) As Boolean
Dim rv As Boolean, cell As Range
For Each cell In haystack
If cell = needle Then
rv = True
Exit For
End If
Next cell
InRange = rv
End Function |
Function InRange(needle As Variant, haystack As Range) As Boolean
Dim rv As Boolean, cell As Range
For Each cell In haystack
If cell = needle Then
rv = True
Exit For
End If
Next cell
InRange = rv
End Function
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2017-11-12, 00:37
Vor ein paar Wochen habe ich ein kleines Bestelltool in Excel gebaut, um die Bestellungen bei Danielz‘ Foodtruck zu vereinfachen.
Ausgangspunkt ist eine kleine Tabelle, in der die einzelnen Gerichte mit den Preisen aufgeführt sind. Über die Menge wird dann der jeweilige Preis ausgerechnet und die Summe gebildet. Es sind verschiedene Ranges definiert (für die Ziel-E-Mail-Adresse, den Standard-Betreff, etc.) die wichtigste ist aber die Auswahl-Range, die die gesamte Tabelle mit den Gerichten umfasst.
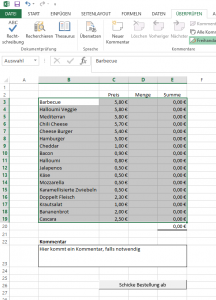
Mit ein wenig VBA wird dann die Outlook-Mail erzeugt.
Den Namen des Benutzers könnte man theoretisch per VBA.Environ("Username") ermitteln, dies liefert aber nur das Login und nicht den Klarnamen. Dazu ist eine Abfrage des Active Directory (siehe https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/2007.08.heyscriptingguy.aspx) notwendig:
Function GetUsername()
Set objAD = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
Set objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & objAD.UserName)
GetUsername = objUser.DisplayName
End Function |
Function GetUsername()
Set objAD = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
Set objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & objAD.UserName)
GetUsername = objUser.DisplayName
End Function
Über die getOrder() Funktion erstellen wir den String für den jeweiligen Besteller aus der Tabelle.
Function getOrder()
auswahl = Range("Auswahl")
bestellstring = "* " & GetUsername() & ": "
Order = 0
For i = 1 To UBound(auswahl)
If (auswahl(i, 3)) > 0 Then
If Order > 0 Then
bestellstring = bestellstring & ", "
End If
bestellstring = bestellstring & auswahl(i, 3) & " x " & auswahl(i, 1)
Order = 1
End If
Next i
Debug.Print bestellstring
getOrder = bestellstring
End Function |
Function getOrder()
auswahl = Range("Auswahl")
bestellstring = "* " & GetUsername() & ": "
Order = 0
For i = 1 To UBound(auswahl)
If (auswahl(i, 3)) > 0 Then
If Order > 0 Then
bestellstring = bestellstring & ", "
End If
bestellstring = bestellstring & auswahl(i, 3) & " x " & auswahl(i, 1)
Order = 1
End If
Next i
Debug.Print bestellstring
getOrder = bestellstring
End Function
Im letzten Schritt gilt es nur noch, den erzeugten String per Mail zu versenden. Hier waren die Code-Schnipsel von http://www.rondebruin.nl/win/winmail/Outlook/tips.htm sehr hilfreich. Hinweis: Der Button im Bestellformular ist an diese Sub gebunden.
Sub Mail_small_Text_Outlook()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Dim strbody As String
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
strbody = "Hier ist meine Bestellung:" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & vbNewLine
body = getOrder()
If Len(Range("kommentar") > 0) Then
body = body & vbNewLine & Range("kommentar")
End If
On Error Resume Next
With OutMail
.To = Range("receiver")
.CC = ""
.BCC = ""
.Subject = Range("subject")
.body = strbody & body
.Display
End With
On Error GoTo 0
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End Sub |
Sub Mail_small_Text_Outlook()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Dim strbody As String
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
strbody = "Hier ist meine Bestellung:" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & vbNewLine
body = getOrder()
If Len(Range("kommentar") > 0) Then
body = body & vbNewLine & Range("kommentar")
End If
On Error Resume Next
With OutMail
.To = Range("receiver")
.CC = ""
.BCC = ""
.Subject = Range("subject")
.body = strbody & body
.Display
End With
On Error GoTo 0
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End Sub
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2017-10-22, 15:42
Ich arbeite momentan an einer kleinen Excel-Anwendung, um die wöchentliche Bestellung von meinen Kollegen und mir bei „Danielz Foodtruck“ (https://www.facebook.com/Danielz-Food-Truck-709172459137209/) zu optimieren. Mit reinem VBA kommt man leider nur an den Login-Namen, nicht aber an den eigentlichen Namen des Nutzers:
Sub showUsername()
MsgBox VBA.Environ("Username")
End Sub |
Sub showUsername()
MsgBox VBA.Environ("Username")
End Sub
Die Information steht jedoch im Active Directory, mit ein paar Zeilen VBA (Quelle: https://community.spiceworks.com/topic/361258-using-vba-to-report-user-s-full-name-maybe-from-ad) kann man sie abfragen:
Function GetUsername()
Set objAD = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
Set objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & objAD.UserName)
GetUsername = objUser.DisplayName
End Function |
Function GetUsername()
Set objAD = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
Set objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & objAD.UserName)
GetUsername = objUser.DisplayName
End Function
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2017-07-30, 17:56
Als TeXie mag man es nicht glauben, aber in Powerpoint gibt es keine eingebaute Möglichkeit, die Gesamtzahl der Folien auf der Folie selbst auszugeben. Über den Umweg VBA geht es (gefunden unter https://superuser.com/questions/130489/insert-total-number-of-slides-in-powerpoint-2007)
Sub numberSlides()
' https://superuser.com/questions/130489/insert-total-number-of-slides-in-powerpoint-2007
' run with F5
Dim s As Slide
Dim shp As Shape
For Each s In ActivePresentation.Slides
s.DisplayMasterShapes = True
s.HeadersFooters.SlideNumber.Visible = msoTrue
For Each shp In s.Shapes
If Left(shp.Name, 12) = "Slide Number" Then
shp.TextFrame.TextRange.Text = s.SlideNumber & " von " & ActivePresentation.Slides.Count
End If
Next
Next
End Sub
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
Category:
MS Office & VBA |
Kommentare deaktiviert für Gesamtfolienzahl in Powerpoint einfügen
2016-05-01, 10:06
Hier ein kurzes Beispiel für die Nutzung der Rest() Funktion, um Formeln in Excel nur auf jede x-te Zeile anzuwenden.
- Mit
zeile() erhält man die Zeilennummer des aktuellen Bezugs
Rest() gibt den Rest bei der ganzzahligen Teilung zurückWenn() prüft einfach die Bedingung, ob Rest() einen bestimmten Wert hat
Man kann nicht nur gerade/ungerade prüfen (oberes Beispiel), auch bei anderen Zeilensprüngen klappt das.

Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
Category:
MS Office & VBA |
Kommentare deaktiviert für Excel: Formel nur auf die x-te Zeile anwenden
2016-04-24, 17:14
Eine Aufgabe für zwischendurch: Wie kann man ein bestehendes Excel-Blatt in eine Anzahl von anderen Excel-Dateien kopieren?
- Definiere eine benannte Zell-Range, hier „Workbooks“ genannt
- In dieser Liste trage alle Excel-Dateien ein, in die das Muster-Blatt (hier „Template“ genannt) kopiert werden soll.
Hinweis: Ich habe diese Liste mit dir /b *.xlsx erzeugt.
- Setze einen Button in das Sheet und hinterlege als Code das folgende
- Wichtig: Die aktuelle Arbeitsmappe mit dem Button und der Liste liegt im selben Verzeichnis wie die Ziel-Dateien. Wenn nicht, dann muss der Pfad angepasst werden.
Sub Schaltfläche1_Klicken()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Range("Workbooks")
MsgBox (c.Value)
Set kopiereWas = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Template")
Set kopiereWohin = Workbooks.Open(Application.ActiveWorkbook.Path + "\\" + c.Value)
kopiereWas.Copy kopiereWohin.Sheets(1)
Next c
End Sub |
Sub Schaltfläche1_Klicken()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Range("Workbooks")
MsgBox (c.Value)
Set kopiereWas = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Template")
Set kopiereWohin = Workbooks.Open(Application.ActiveWorkbook.Path + "\\" + c.Value)
kopiereWas.Copy kopiereWohin.Sheets(1)
Next c
End Sub
Hinweis: Die Ziel-Arbeitsmappe wird hier nicht geschlossen, werde ich zusammen mit Screenshots nachliefern.
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
Category:
MS Office & VBA |
Kommentare deaktiviert für Excel VBA: Blatt in Liste von Excel Dateien kopieren
2015-11-21, 22:57
A PDF with the most important Excel shortcuts: http://www.thecompanyrocks.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/CR-Updated-Chart-of-Popular-Excel-Keyboard-Shortcuts.pdf
Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website
2015-03-21, 20:22
Die folgende Excel-Funktion ist nützlich, um innerhalb von Excel Strings in ihre Bestandteile zu zerlegen.
Function SplitteString(zeichenkette, separator, vorkommen) As String
Dim feld() As String
feld = Split(zeichenkette, separator)
SplitteString = feld(vorkommen - 1)
End Function

Uwe Ziegenhagen likes LaTeX and Python, sometimes even combined.
Do you like my content and would like to thank me for it? Consider making a small donation to my local fablab, the Dingfabrik Köln. Details on how to donate can be found here Spenden für die Dingfabrik.
More Posts - Website






